DeepSeek-R1 v OpenAI o1: Which AI Model is Better?
This comparison dives into these AI model's features, including performance, capabilities, accessibility, and pricing.
The rapid growth of artificial intelligence has led to the rise of powerful large language models (LLMs), each specifically built for different needs and priorities. Among the most talked about models today are DeepSeek R1 and OpenAI’s O1, both with advanced AI-driven capabilities.
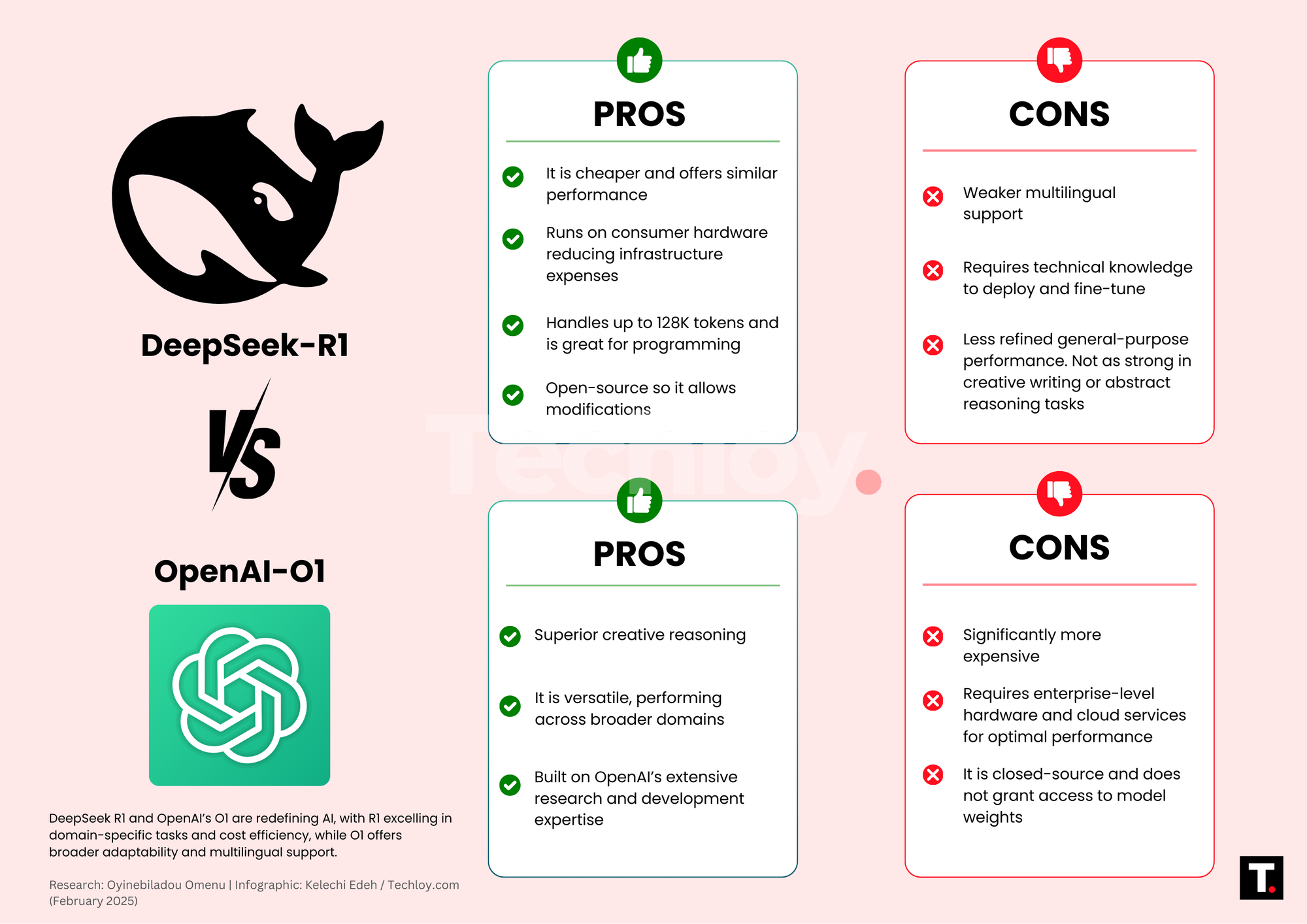
While DeepSeek R1 excels in domain-specific applications and is cost-efficient, OpenAI’s O1 is more generalized, has multilingual support, and an easier integration. Understanding the strengths and limitations of these models is necessary for researchers and developers looking to utilize these AI models.
A comparison between DeepSeek R1 and OpenAI o1 Models
#1: Performance
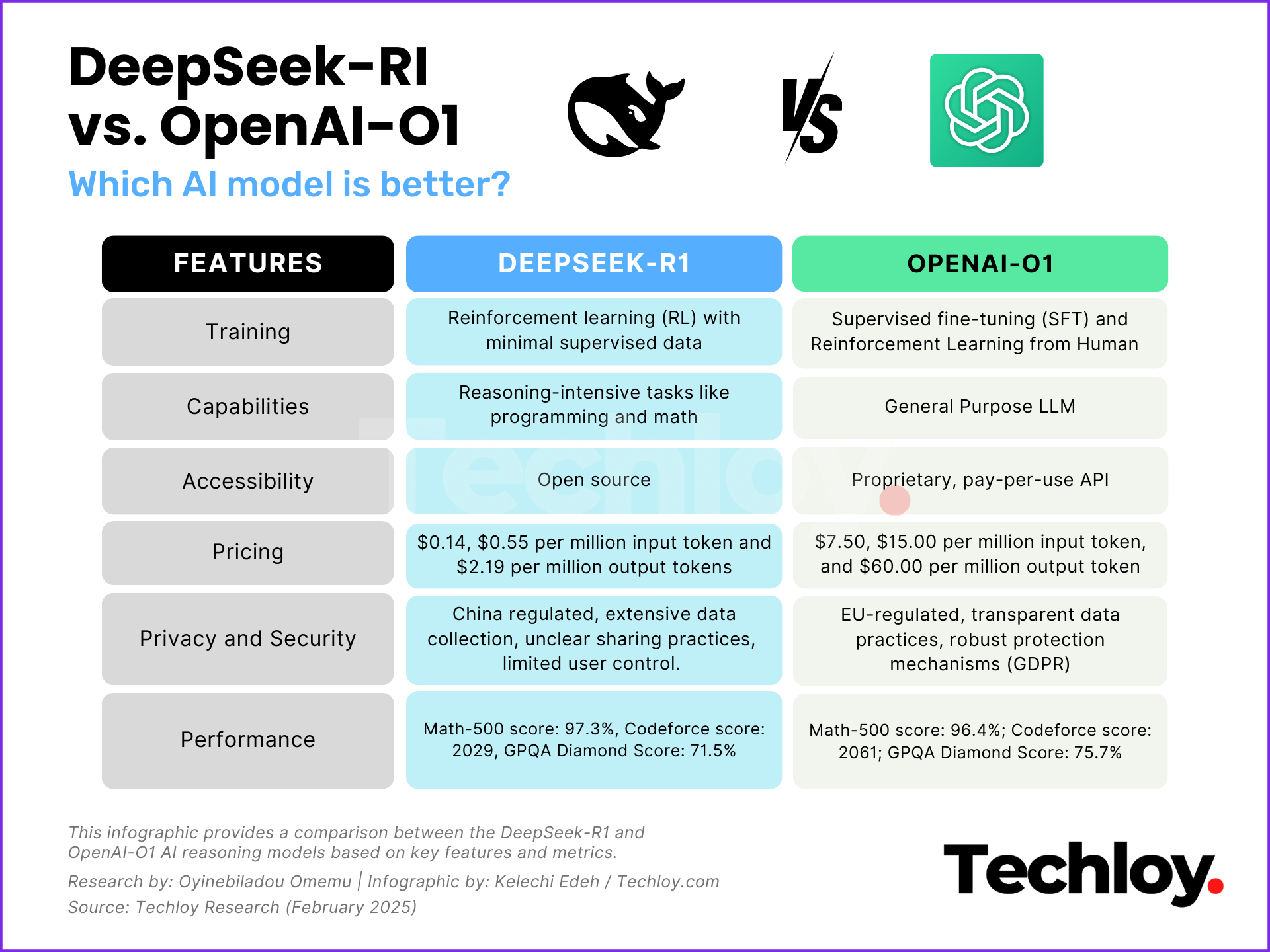
One of the primary benchmarks for AI models is their ability to handle complex coding and mathematical reasoning tasks. OpenAI o1 excels in coding and mathematical tasks, outperforming DeepSeek r1 on Codeforces with a 2727 Elo rating versus r1’s 2029. It also achieved 96.7% on the AIME benchmark, compared to R1’s 79.8%.
#2: Accessibility
DeepSeek-R1 is open-source, allowing developers to download, modify, and deploy models freely, supporting localized deployment on standard devices. This enhances accessibility, and innovation, and promotes transparency. OpenAI o1, however, is closed-source, available only via paid APIs and platforms like Microsoft Azure, limiting on-premises deployment options.
#3: Pricing
DeepSeek-R1 is significantly more cost-effective. It charges $0.14 to $0.55 per 1 million input tokens and $2.19 per 1 million output tokens. In contrast, OpenAI o1 costs between $7.50 and $15 per 1 million input tokens and $60 per 1 million output tokens, making DeepSeek-R1 the budget-friendly option with nearly equal performance.
#4: Architecture
The design and training methodologies of these models contribute to their distinct performance capabilities. DeepSeek-R1 uses a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture and reinforcement learning, activating only task-specific parameters to optimize computational costs. It is trained on hybrid datasets, including domain-specific data, and employs optimization techniques that boost efficiency by 45x. OpenAI o1, on the other hand, relies on a dense transformer architecture with over a trillion parameters, trained on vast datasets.
#5: Capabilities
DeepSeek R1 excels in specialized domains like mathematics, science, and programming but struggles to generalize across diverse topics without fine-tuning. Its open-source nature allows customization, but the built-in performance remains domain-specific. In contrast, OpenAI’s O1 is highly versatile, adapting well to a wide range of tasks without additional modifications. Its extensive training enables generalization, making it more suitable for general-purpose AI applications.
#6 Privacy and Security
The DeepSeek-R1 model and OpenAI's o1 model differ significantly in terms of privacy and security. DeepSeek-R1 raises concerns with its data storage in China, extensive user data collection, and unclear data-sharing practices. In contrast, OpenAI regulated by EU laws, prioritizes transparency, user control, and robust data protection, providing clearer opt-out options, data deletion mechanisms, and General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) compliance.
Conclusion
Both DeepSeek R1 and OpenAI’s O1 offer compelling benefits, but the right choice depends on specific use cases and priorities. DeepSeek R1 is the best option for those seeking cost-effective, open-source AI with strong domain expertise in specialized fields like programming and mathematics. In contrast, OpenAI’s O1 is ideal for users needing a more generalized, multilingual model.









