Nvidia GTC 2025: All the announcements from Jensen Huang's keynote
This year, Nvidia is making a massive push toward open-source AI and quantum computing innovations.
Jensen Huang, Nvidia’s CEO, finally took the stage at Nvidia GTC 2025, and you can bet the announcements had the crowd in awe from start to finish.
While Nvidia is known for pushing the limits of GPU technology, this year’s event took things to another level—unveiling everything from humanoid home robots to personal AI supercomputers. As expected, the company also introduced new AI chip architectures, showcased bold strides in quantum computing, and much more.
Here’s a look at some of the most jaw-dropping reveals from Huang’s keynote.
Personal AI Supercomputers
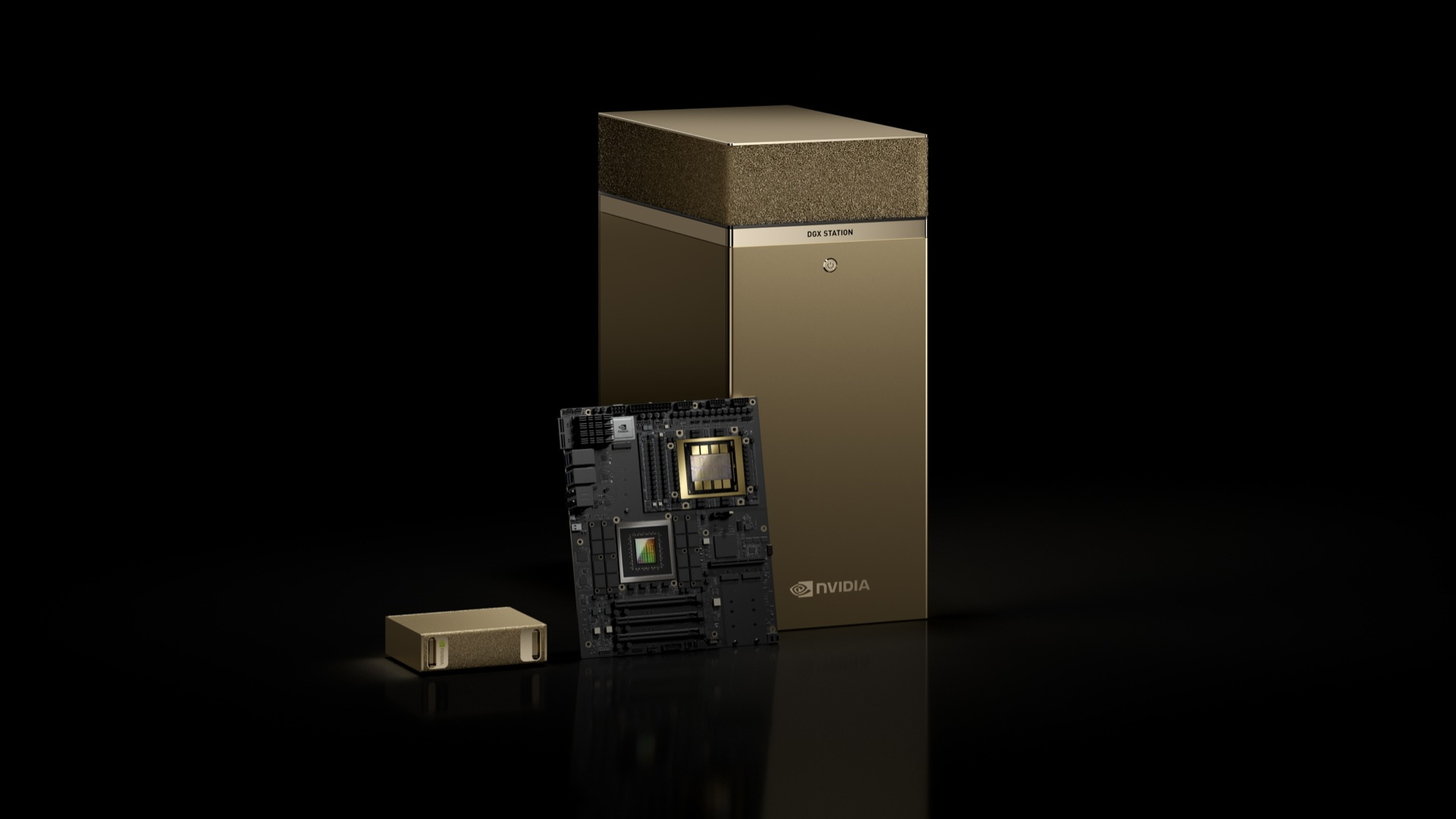

At the Keynote, Huang unveiled Nvidia’s brand-new “personal AI supercomputers,” DGX Spark and DGX Station, built on the Grace Blackwell platform. Nvidia introduced these two AI supercomputers to bridge the gap between local and cloud-based AI workflows, making high-performance AI more accessible to researchers, developers, and students.
DGX Spark is the world's smallest AI supercomputer, delivering up to 1,000 trillion operations per second. While DGX Station is designed for high-performance AI development, featuring 784GB of memory and 800Gb/s networking speeds. DGX Spark is available now, while DGX Station will roll out later in 2025 through partners like Asus, Dell, HP, and Lenovo.
The Rubin AI Chips: The Next Leap in AI Hardware
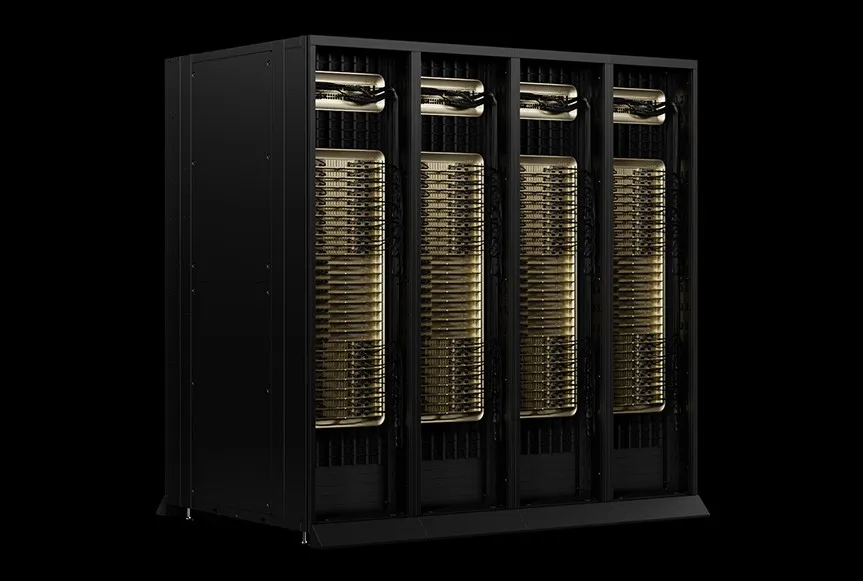

Of course, it wouldn’t be an Nvidia keynote without some groundbreaking chip announcements. Huang introduced Blackwell Ultra (arriving later in 2025) and its successor, Vera Rubin, named after the legendary astronomer. Rubin is expected in late 2026, with Rubin Ultra following in 2027.
For those keeping score, Rubin will deliver 50 petaflops of AI inferencing power, which is more than double what Nvidia’s current Blackwell chips offer. If you thought AI was moving fast, buckle up.
And just when you think that’s all, Huang teased Feynman GPUs, set to arrive in 2028.
Meet Groot N1 - AI is Now “Thinking Fast and Slow”
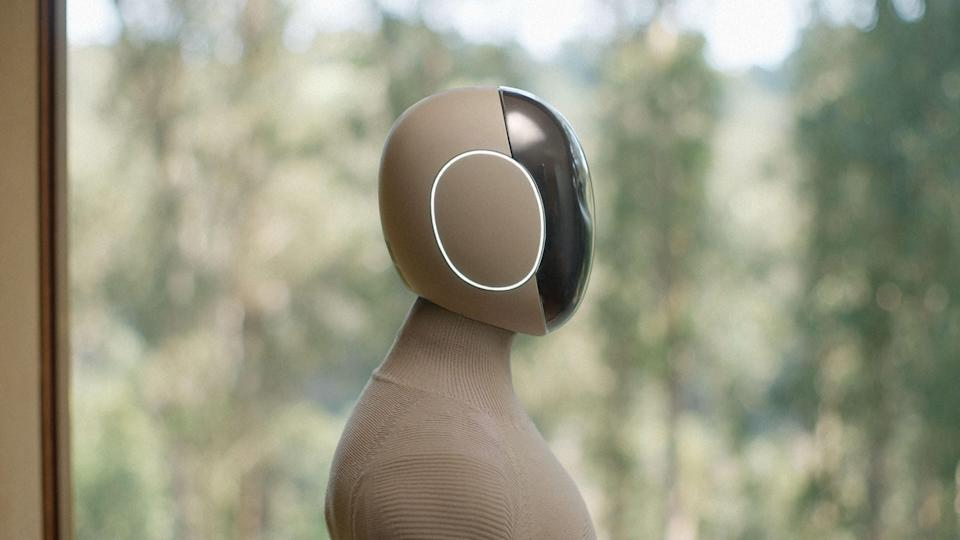

We’ve all seen humanoid robots struggle with stairs, but Nvidia believes its new Groot N1 foundation model is about to change that. Groot N1 is a generalist AI model designed to help humanoid robots navigate the real world with more intelligence, perception, and reasoning.
Its dual-system architecture is inspired by human cognition, one part processes information slowly and carefully, while the other handles fast reflexive decisions. It’s Nvidia’s biggest leap yet into robotics, and the best part is that Groot N1 is open-source.

Nvidia Expands into Quantum Computing
In a significant step toward the future of computing, Nvidia announced the Nvidia Accelerated Quantum Research Center (NVAQC) in Boston and is set to begin operations later this year. This research hub will integrate AI supercomputing with quantum hardware, tackling some of quantum computing’s most pressing challenges, such as qubit noise and quantum error correction.
Collaborators include Quantinuum, Quantum Machines, QuEra Computing, Harvard Quantum Initiative, and MIT’s Engineering Quantum Systems group. By leveraging Nvidia GB200 NVL72 rack-scale systems and CUDA-Q development tools, NVAQC aims to accelerate quantum-classical hybrid computing.
As Jensen Huang described it, “Quantum computing will augment AI supercomputers to tackle some of the world’s most important problems, from drug discovery to materials development.”
Disney Joins the AI Party with Newton Physics Engine
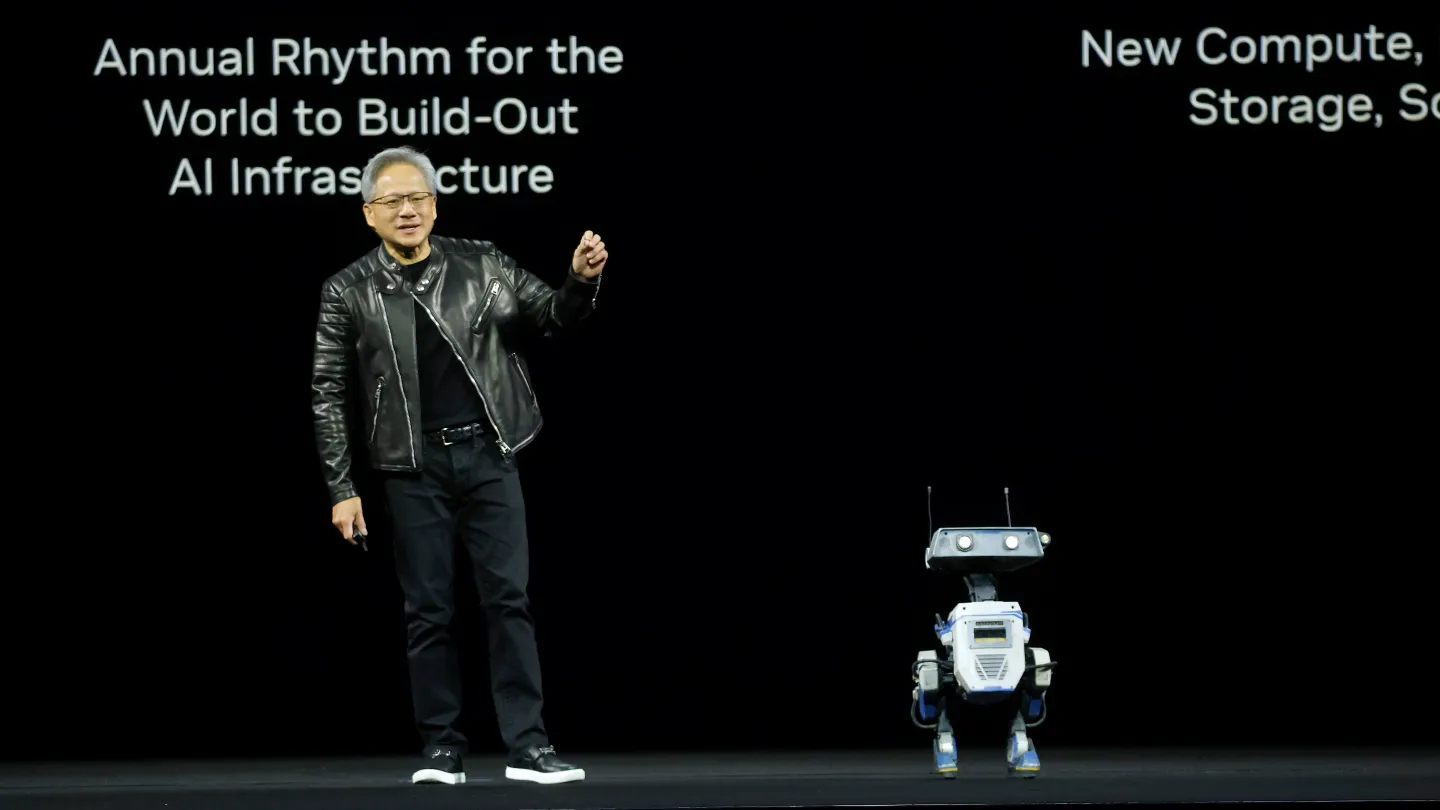
In a move straight out of sci-fi, Nvidia is collaborating with Disney Research and Google DeepMind on Newton, a next-gen physics engine for robotics. If you’ve ever seen those adorable Star Wars-inspired droids at Disney theme parks, Newton will help make them smarter and more expressive.
Disney is gearing up to showcase BDX droids (yes, real Star Wars-style bots) in its theme parks next year. Newton will also support robots handling tricky materials like cloth, food, and even sand.
Want to tinker with it? Nvidia is releasing Newton as open-source later this year.
Conclusion
This year, Nvidia is making a massive push toward open-source AI and quantum computing innovations. From the Groot N1 robotics model to the Newton physics engine and CUDA-Q for quantum computing, Nvidia is doubling down on democratizing access to AI tools. The company’s shift toward open-source solutions makes you wonder if it is a strategic move to counterbalance the DeepSeek effect on its open-source model.
The growing influence of DeepSeek in AI research has put pressure on Nvidia to remain at the forefront of innovation. While Nvidia’s traditional dominance has relied on proprietary hardware and software, the rise of competitive open-source models may be driving this new strategy. However, notwithstanding the market challenges and competition, Nvidia is not slowing down, as we see with the interesting announcements by Hunag.






